Unsafe Acts and Unsafe Conditions – All You Need to Know
Workplace safety is of paramount importance for safeguarding employees and fostering a productive environment. To achieve this, it is crucial to address two key aspects: unsafe acts and unsafe conditions. Understanding the difference between these terms is fundamental to promoting a safe working environment.
Let’s define what each of these mean:
What are Unsafe Acts?
Unsafe acts refer to actions or behaviors that deviate from established safety protocols. These actions can range from disregarding safety guidelines to failing to use PPE correctly. Such acts not only jeopardize the individual involved but also pose risks to the entire workforce.
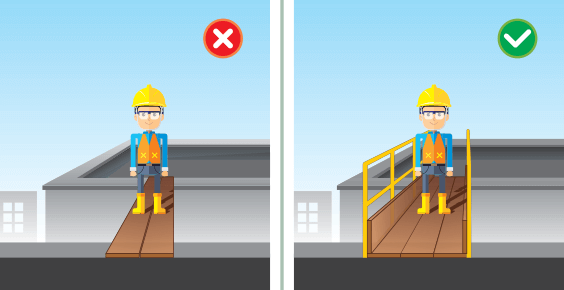
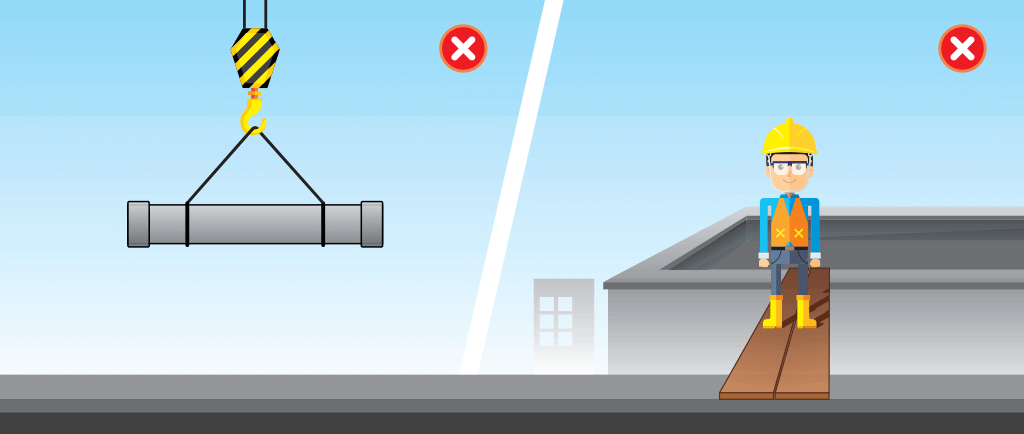
What are Unsafe Conditions?
Unsafe conditions encompass physical elements within the workplace that have the potential to cause harm. These may include poor housekeeping, inadequate lighting or ventilation, malfunctioning equipment, or improper handling of hazardous materials. Identifying and rectifying these conditions is essential to ensure the safety and well-being of employees.
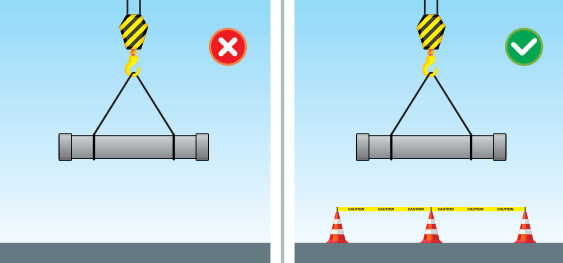
By distinguishing between unsafe acts and unsafe conditions, employers and employees can better comprehend the risks present in their workplace. Now, let’s delve into the significance of recognizing these hazards and the potential consequences that may arise.
See how Safetymint can help in managing incidents
Importance of Identifying Unsafe Acts and Conditions:
Recognizing and addressing unsafe acts and conditions is crucial for maintaining a safe and secure workplace. By proactively identifying these hazards, employers and employees can mitigate risks and prevent potential accidents, injuries, and productivity losses. Let’s explore why it is imperative to prioritize the identification of unsafe acts and conditions:
Accident Prevention:
- Identifying unsafe acts and conditions allows for timely intervention and prevention of accidents and incidents.
- Addressing potential hazards proactively reduces the likelihood of workplace injuries and associated costs.
Employee Well-being:
- Recognizing unsafe acts and conditions demonstrates a commitment to the well-being of employees.
- By creating a safe work environment, employers foster trust, motivation, and job satisfaction among their workforce.
Increased Productivity:
- A safe workplace promotes productivity by reducing interruptions caused by accidents or injuries.
- By eliminating potential risks, employees can focus on their tasks without the fear of harm, leading to improved efficiency.
Legal Compliance:
- Identifying and addressing unsafe acts and conditions ensures compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
- Failure to address hazards can result in legal consequences, fines, or reputational damage for organizations.
Cost Savings:
- Proactively identifying unsafe acts and conditions helps avoid costs associated with workplace incidents, such as medical expenses, worker’s compensation claims, or litigation.
- Creating a culture of safety can also reduce insurance premiums over time.
Continuous Improvement:
- Recognizing and rectifying unsafe acts and conditions paves the way for continuous improvement in safety practices.
- By learning from past incidents and near misses, organizations can implement preventive measures and enhance their safety protocols.
In our next section, we will discuss common examples of unsafe acts and unsafe conditions.

Examples of common Unsafe Acts:
Some examples of unsafe acts commonly observed in workplaces include the following:
Not using personal protective equipment correctly or at all:
- Neglecting to wear safety goggles, helmets, gloves, or other necessary protective gear.
- Potential risks: Eye injuries, head trauma, burns, cuts, exposure to harmful substances.
Disregarding safety procedures and protocols:
- Ignoring established safety protocols, such as lockout/tagout procedures or confined space entry requirements.
- Potential risks: Equipment malfunction, electrocution, falls, asphyxiation, chemical exposure.
Engaging in horseplay or reckless behavior:
- Engaging in rough or playful activities that distract or endanger oneself and others.
- Potential risks: Trips, falls, collisions, equipment damage, and severe injuries.
Operating machinery or equipment without proper training:
- Using machinery or equipment without adequate knowledge, training, or authorization.
- Potential risks: Crush injuries, amputations, entanglement, electrocution, equipment failure.
Ignoring ergonomic guidelines:
- Failing to follow ergonomic principles while performing tasks, such as lifting heavy objects incorrectly or maintaining poor posture.
- Potential risks: Musculoskeletal disorders, back injuries, strains, sprains, and chronic pain.
Examples of common Unsafe Conditions:
In addition to unsafe acts, there are various unsafe conditions that can compromise workplace safety. It’s crucial to identify and address these conditions promptly to create a safer work environment. Let’s explore some common examples of unsafe conditions:
Poor housekeeping, leading to slips, trips, and falls:
- Cluttered workspaces, obstructed walkways, or spilled liquids can increase the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
- Potential hazards: Sprained or broken bones, head injuries, back injuries, and bruises.
Inadequate lighting or ventilation:
- Inadequate lighting can make it difficult to identify potential hazards or see warning signs, while poor ventilation can lead to air quality issues.
- Potential hazards: Increased likelihood of accidents due to reduced visibility, respiratory problems, eye strain, and fatigue.
Defective or malfunctioning equipment:
- Equipment that is not properly maintained or repaired can pose significant risks to employees.
- Potential hazards: Equipment malfunctions, electrical shocks, burns, and injuries caused by faulty machinery.
Improper storage or handling of hazardous materials:
- Failure to follow proper procedures for storing and handling hazardous materials can lead to accidents and exposure risks.
- Potential hazards: Chemical spills, fires, explosions, skin irritation, respiratory problems, and long-term health issues.
In our next section, we will learn about the potential consequences and why reporting and correcting these hazards is crucial.
Importance of Reporting and Correcting:
Reporting unsafe acts and conditions and taking prompt corrective measures are crucial for maintaining a safe work environment. Everyone in the organization, from management to employees, plays a vital role in ensuring workplace safety. Let’s explore the importance of reporting and correcting unsafe acts and conditions:
Early Intervention:
- Reporting unsafe acts and conditions at the earliest opportunity allows for timely intervention and mitigation of potential risks.
- Identifying and addressing hazards promptly can prevent accidents, injuries, and illnesses before they occur.
Preventing Recurrence:
- Reporting unsafe acts and conditions helps identify underlying causes and patterns, enabling organizations to implement preventive measures.
- By addressing root causes, organizations can break the cycle of repeated incidents and create a safer work environment.
Accountability and Responsibility:
- Reporting unsafe acts and conditions fosters a culture of accountability and shared responsibility among all employees.
- It encourages individuals to take ownership of their own safety and the safety of their colleagues.
Continuous Improvement:
- Reporting unsafe acts and conditions provides valuable data for analyzing trends, identifying systemic issues, and improving safety protocols.
- Regular reporting and corrective actions lead to an ongoing cycle of improvement, ensuring a safer workplace over time.
Open Communication:
- Reporting unsafe acts and conditions encourages open communication between employees and management.
- It creates a supportive environment where employees feel comfortable raising concerns and suggestions for improving safety.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
- Reporting unsafe acts and conditions is often a legal requirement to ensure compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
- Organizations that prioritize reporting and corrective actions demonstrate their commitment to meeting legal obligations.
Remember, reporting should not be seen as punitive but as a means of preventing harm and creating a safer work environment for all. Employers should encourage employees to report without fear of reprisal and provide clear channels for reporting, such as anonymous reporting mechanisms or safety suggestion boxes.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.