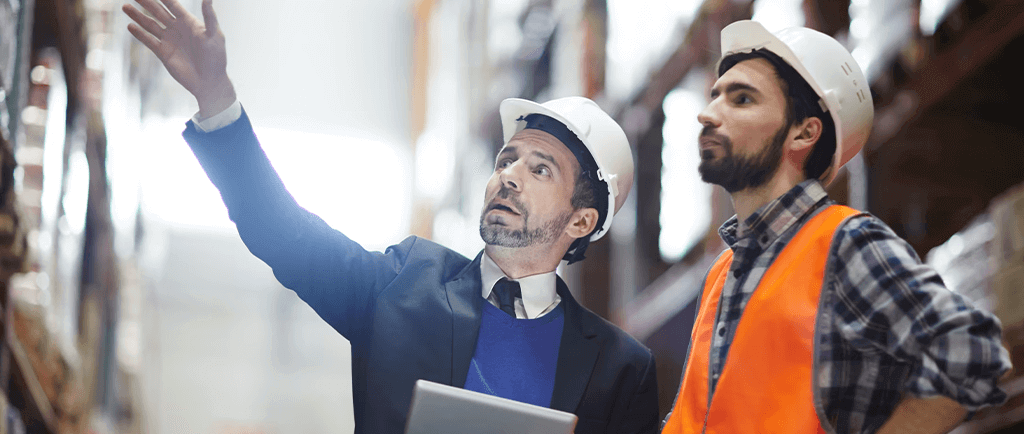
Roles and Responsibilities of an EHS Manager
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Management is a vital field where EHS Managers play a critical role in maintaining the balance of safety, health, and environmental integrity. Their job is not just a responsibility but a mission to uphold the highest standards in workplace safety and environmental stewardship. In this dynamic domain, EHS Managers work tirelessly to navigate a complex landscape of regulations and risks, ensuring their organizations remain both safe and compliant.
In this blog post, I aim to shed light on the multifaceted duties of EHS Managers. We’ll delve into their roles, from ensuring strict adherence to compliance requirements to implementing advanced technology for improved safety measures. We also explore the unique challenges EHS Managers face in their quest to foster a workplace environment that prioritizes safety, compliance, and sustainability.
Who is an EHS Manager?
An EHS Manager is the go-to person in an organization for all things related to workplace safety and environmental care. They are the champions of creating a safe, healthy, and eco-friendly work environment. These managers wear many hats, ensuring that a company not only meets legal safety standards but also cares for its employees’ well-being and the planet. Think of them as the guardians of the workplace, tirelessly working behind the scenes to make sure everyone stays safe and the environment remains protected.
Roles of an EHS Manager:
As an EHS Manager, the role encompasses a diverse range of responsibilities, all aimed at fostering a safe and environmentally responsible workplace.
Here are some of the key roles they play:
Developing Safety Policies: Crafting and implementing policies and procedures that ensure a safe working environment.
Risk Assessment: Identifying potential hazards in the workplace and devising strategies to mitigate these risks.
Compliance Management: Ensuring that the organization adheres to all relevant health, safety, and environmental laws and regulations.
Emergency Response Planning: Creating and maintaining emergency response plans for various potential incidents.
Employee Training and Engagement: Conducting training sessions for employees on safety practices and promoting a culture of safety awareness.
Incident Investigation and Reporting: Investigating workplace incidents or accidents and reporting findings to appropriate parties.
Environmental Management: Implementing strategies for waste management, pollution control, and sustainable practices.
Health and Wellness Programs: Developing programs to support employee health and wellness.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and updating EHS policies and procedures to improve safety standards.
Stakeholder Communication: Communicating effectively with employees, management, and external stakeholders about EHS matters.
Importance of Compliance:
Compliance is a fundamental aspect for EHS Managers, serving as the backbone of their role. It involves ensuring that the organization adheres to a variety of health and safety regulations. This isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about creating a safe environment for employees and preventing legal troubles. By keeping up with the latest laws and standards, EHS Managers help their organizations avoid costly fines and maintain a positive reputation.
Risk Assessment and Management:
In risk assessment and management, EHS Managers play a detective role, identifying potential hazards in the workplace. They meticulously analyze various scenarios to pinpoint risks, ranging from minor injuries to major environmental impacts. Once identified, they strategize on how to minimize or eliminate these risks. This proactive approach not only safeguards employees but also helps in averting significant financial and reputational damage to the organization.
Training and Awareness
Training and awareness are the cornerstones of EHS Management. EHS Managers conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about potential hazards and safe practices. This is not just a one-off event but an ongoing process to instill a culture of safety. By keeping safety at the forefront of employees’ minds, they ensure that safety guidelines are more than just words on a page; they’re actions that protect lives every day.
Sustainability and Environmental Management
Sustainability and environmental management are more than just buzzwords for EHS Managers. They are tasked with implementing green practices, such as waste reduction, efficient resource utilization, and pollution prevention. Their role extends to ensuring the company operates in an environmentally responsible manner, which not only benefits the planet but also enhances the company’s image and compliance with environmental laws.
Technology in EHS Management
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern EHS Management. EHS Managers leverage various software and technological tools to streamline safety processes. From tracking incidents and maintaining records to analyzing data for insights, technology empowers them to manage safety more effectively and efficiently. It allows for real-time monitoring and quicker responses, making the management of health and safety more dynamic and data-driven.
Challenges Faced by EHS Managers
EHS Managers routinely encounter a multitude of challenges. They must navigate constantly changing legal landscapes, adapt to diverse workplace environments, and manage varying degrees of risks. Additionally, they face the task of fostering a safety culture in an organization where employees from different backgrounds and skill levels may have varying attitudes towards safety. Balancing these challenges while ensuring compliance and maintaining a safe work environment is a testament to their vital role in any organization.
In conclusion, the role of an EHS Manager is multifaceted and vital, blending compliance, risk management, training, sustainability, and technology to maintain a safe and responsible workplace. Despite the challenges, their dedication plays a crucial role in fostering a culture of safety and environmental stewardship, ultimately driving the well-being and success of any organization.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.