Leading and Lagging Indicators in Safety – All You Wanted to Know
Safety is a critical aspect of any workplace, and organizations are always looking for ways to enhance their safety programs and reduce the risk of incidents and injuries. One tool that can be useful in achieving this goal is the use of leading and lagging indicators.
What is a leading indicator?
A leading indicator is a metric or measure that predicts future trends or changes. In safety, leading indicators are used to identify potential risks or hazards and take proactive measures to prevent incidents and injuries, rather than just reacting to incidents that have already occurred (which are known as lagging indicators).
Some examples of leading indicators include:
- Unsafe act
- Unsafe condition
- Near miss reporting
- Safety observation and feedback
- Pre-task hazard analysis
- Safety training participation and completion
- Safety suggestion program participation and implementation
- Compliance with safe work procedures and policies.
See how Safetymint can help in managing incidents
Benefits of tracking leading indicators:
The benefits of tracking leading indicators in safety include improved identification of potential hazards, early warning of emerging trends and risks, enhanced proactive safety management, increased employee engagement and involvement, improved safety culture and leadership commitment, and enhanced continuous improvement and goal setting processes.
What is a lagging indicator?
A lagging indicator is a metric or measure that reflects past events and provides information about what has already happened. In safety, lagging indicators are used to evaluate the effectiveness of safety efforts after incidents or injuries have occurred.
Examples of lagging indicators in safety include:
- Total recordable injury rate (TRIR)
- Lost time injury rate
- First aid case
- Fire hazard
- Property damage cost
- Workers’ compensation claims cost.
Benefits of tracking lagging indicators:
The benefits of tracking lagging indicators in safety include evaluation of safety performance and impact, measurement of the effectiveness of safety efforts, identification of areas for improvement, identification of safety performance trends over time, provision of data for benchmarking and comparison, and development of safety goals and targets.
Difference between leading and lagging indicators:
Timing: Leading indicators predict future trends and events, while lagging indicators reflect past events.
Purpose: Leading indicators are used to identify potential hazards and prevent incidents, while lagging indicators are used to evaluate safety performance after incidents occur.
Focus: Leading indicators focus on proactive safety measures, while lagging indicators focus on reactive measures after incidents occur.
Information: Leading indicators provide early warning of emerging trends, while lagging indicators provide information about past events.
Management: Leading indicators are used to improve safety management, while lagging indicators are used to evaluate safety management effectiveness.
Tracking Leading and Lagging Indicators on Safetymint:
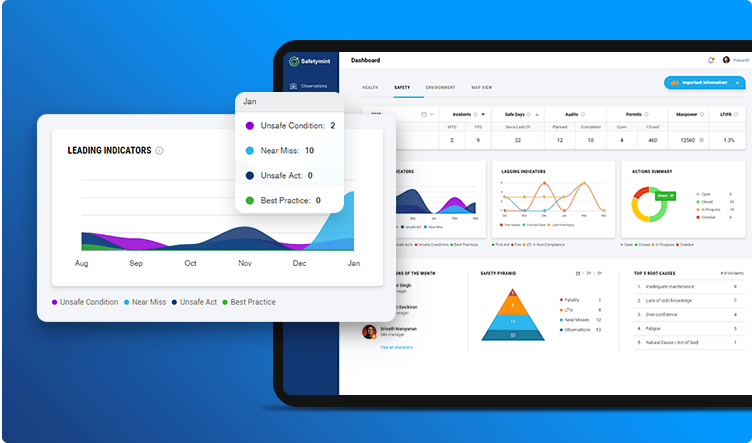
At Safetymint, we provide a user-friendly interface that allows organizations to input and monitor leading and lagging indicators for continuous improvement. The indicators are displayed on the dashboard for easy evaluation by safety officers and the management.
To experience this yourself, request for a free trial, today.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.